Investigating environmental links to disease
Our ground-breaking, multidisciplinary research answers important questions on how chemicals and contaminants in our homes and environment affect fertility, pregnancy, fetal and child development, and health equity. We prioritize filling gaps in knowledge that support clinical decision-making and public policy.
We have written or contributed to more than 180 studies on health and the environment with 23 studies published in peer-reviewed journals in 2020 alone.
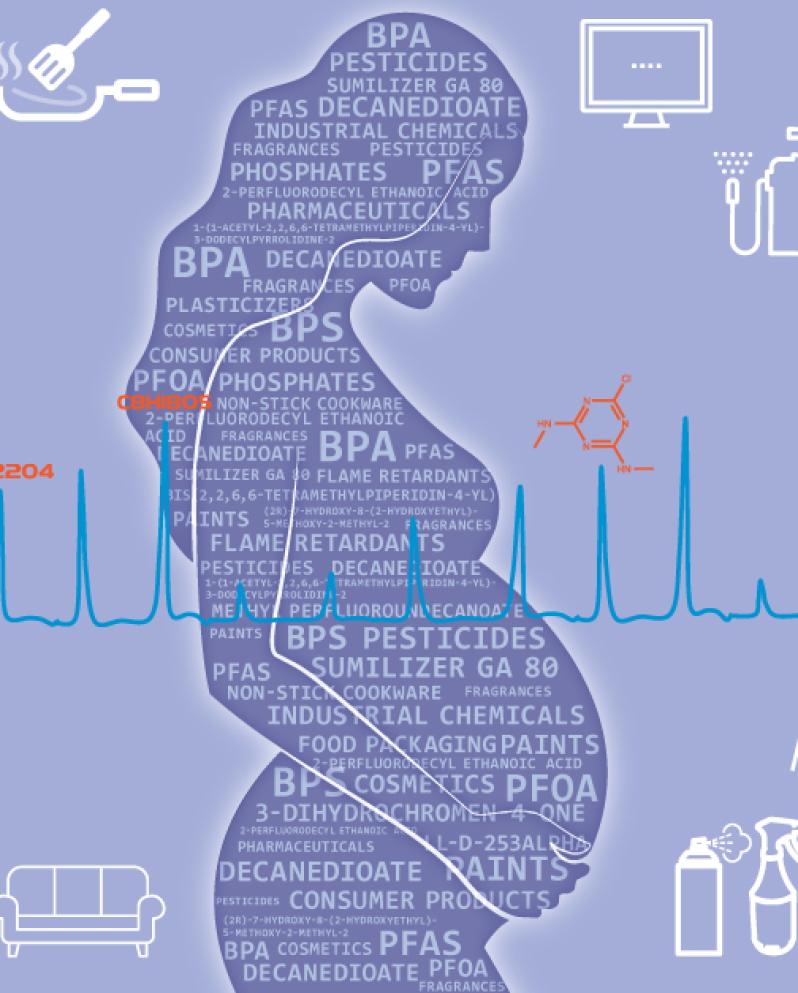
UCSF Study Finds Evidence of 55 Chemicals Never Before Reported in People
Scientists at UC San Francisco have detected 109 chemicals in a study of pregnant women, including 55 chemicals never before reported in people and 42 “mystery chemicals,” whose sources and uses are unknown. The chemicals most likely come from consumer products or other industrial sources.
The study was published March 17 in Environmental Science & Technology.
Major Research Areas

Chemicals
We study how harmful chemicals put into our air, food, water, homes, products, and workplaces affect pregnancy, child development, and health.

Plastics
Plastics are a petro-chemical product packed with endocrine-disrupting chemicals that can harm pregnancy, birth outcomes, neurodevelopment, and immune systems.

Climate and Wildfires
We examine how climate is impacting women's and children's health and how to protect pregnant people from wildfire smoke.
Key Research Projects

ECHO
The Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) is the largest NIH-funded study to date to explore how chemicals and pollutants in our environment impact pregnancy and child development.

DREAM
The Discovering cancer Risks from Environmental contaminants And Maternal/child health (DREAM) project collected data to explore how chemicals put in our air, food, and water increase cancer risk.

ENACT Center
In partnership with Stanford University, the Endometriosis Center for Action, Community Engagement and Training (ENACT) will work to improve endometriosis diagnosis and treatment by exploring the origins and environmental links to this disease.

PRHE conducts groundbreaking, multi-disciplinary research that answers important questions of how chemicals and contaminants in our homes and environment affect fertility, pregnancy, and fetal and child development. PRHE also mentors and trains the next generation of environmental health scientists.
Published Studies
Despite the occurrence of wildfires quadrupling over the past four decades, the health effects associated with wildfire smoke exposures during pregnancy remains unknown. Our study of 7923 singleton births in San Francisco between January 1, 2017 and March 12, 2020 examines associations between wildfire smoke exposure during pregnancy and birthweight.
Pregnancy, birth weight, wildfire, SF Bay area
Climate change is accelerating the intensity and frequency of wildfires globally. Understanding how wildfire smoke (WS) may lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes and alterations in placental function via biological mechanisms is critical to mitigate the harms of exposure.
Wildfire, pregnancy, review
Despite their large numbers and widespread use, very little is known about the extent to which per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) can cross the placenta and expose the developing fetus.
Oxidative stress from excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) is a hypothesized contributor to preterm birth. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure is reported to generate ROS in laboratory settings, and is linked to adverse birth outcomes globally. However, to our knowledge, the relationship between PFAS and oxidative stress has not been examined in the context of human pregnancy.
Melamine, melamine derivatives, and aromatic amines are nitrogen-containing compounds with known toxicity and widespread commercial uses. Nevertheless, biomonitoring of these chemicals is lacking, particularly during pregnancy, a period of increased susceptibility to adverse health effects.
Exposure to environmental chemicals during pregnancy adversely affects maternal and infant health, and identifying socio-demographic differences in exposures can inform contributions to health inequities.
Living near or migrating to areas at high risk for wildfires may result in health consequences and increased disparities for pregnant people and their children.
Wildfire, pregnancy, California, preterm birth